Pulse Reading Normal
Control of body temperature -
Core rectal esophageal etc. Hypothermia. 35.0 C 95.0 F . Normal. 36.5-37.5 C 97.7-99.5 F . Fever. 37.5 or 38.3 C 99.5 or 100.9 F . Hyperthermia. Learn about and revise homeostasis body temperature blood glucose diabetes and water balance with GCSE Bitesize Biology. Maintaining internal environments. Homeostasis is the regulation of conditions in the body such as temperature water content and carbon dioxide levels. If body temperature decreased than 34 C or increased than 41 C body cells can not function. Temperature can be measured with a mercury Chemical control. The body produces heat through the metabolism of food. Body metabolism increases in order to produce more heat for the body asThe temperature of the body is regulated by neural feedback mechanisms which operate primarily through the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus contains not only the control mechanisms but also the key temperature sensors. Under control of these mechanisms sweating begins almost precisely atYour body temperature is almost always cooler than the air around you. Only on the rarest of days in Los Angeles is the air around you warmer. Our body can affect or control how much blood flows through our cutaneous vessels the vessels close to our skin . If the vessel is dilated that s vasodilation.Control of body temperature is the first example of homeostasis we will look at in this series. For humans normal body temperature is 37 C. It is important to maintain this temperature as it is the optimum temperature for enzymes involved in many metabolic processes such as respiration.
Body temperature is monitored and controlled by the thermoregulatory centre in the brain. The thermoregulatory centre contains receptors sensitive to the temperature of the blood. The control of body temperature as well as other factors such as blood CO2. concentration or blood glucose concentration is part of a biological mechanism called 3. When body temperature is too low the tiny blood vessels near the surface of the skin capillaries constrict vaso-constriction .Body temperature control in humans is one of the most familiar examples of homeostasis. Normal body temperature hovers around 37 C 98.6 F but a number of factors can affect this value including exposure to the elements hormones metabolic rate and disease leading to excessivelyCore body temperature is found in the blood supplying organs such as the brain and those in the abdominal and thoracic cavities. It is estimated that accompanying every 1 C rise in body temperature is a 10 rise in the rate of enzyme-controlled chemical reactions Marieb and HoehnBody temperature is an indicator of the amount of heat produced by the body in the process of basic metabolism. And the process of its regulation occurs The function of the hypothalamus also includes the control of the work of our entire endocrine and autonomic nervous system and in it in addition toThe homeostatic control of body temperature is essential for survival in mammals and is known to be regulated in part by temperature-sensitive neurons in the hypothalamus. However the specific neural pathways and corresponding neural populations have not been fully elucidated.
However the nightly course of body temperature and macrosleep rhythm is only partly correlated since body temperature is not only a direct effect of the current stage of sleep but also controlled by the circadian rhythm 54 . Skin and core temperature measurement is a useful additional parameterTemperature control is the process of keeping the body at a constant temperature of 37 C. Our body can only stay at a constant temperature if the heat we Although our core temperature must be 37 C our fingers and toes can be colder. This is because energy is transferred from the blood as it travels toControl of Body temperature This covers how both endoderms and ectoderms control their body temperature. Endoderms like us - by detecting changes in theIn humans body temperature is controlled by the thermoregulatory centre in the hypothalamus. When the environmental temperature decreases gradually - The hypothalamus releases a hormone which activates the anterior pituitary gland to release thyroid stimulating hormone TSH .alters body temperature during the inflammatory response and behavioral. states and in response to declining energy homeostasis. This review. summarizes the central nervous system circuit mechanisms controlling the. principal thermoeffectors for body temperature regulation cutaneous.Low body temperature is the plague of the 21st century. People with low body temperature have a weak reaction to even the most ideal medicines and The control center for body temperature lies in the brain and it is known as the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus is alerted to either extreme cold or
Body Temperature Regulation and Fever. Normal Body Temperatures. The mechanisms for regulating body tempera-ture represent a beautifully designed control system. In this chapter we discuss this system as it operates in health and in disease.7. Core body temperature 37 C Thermoreceptors Hypothalamus nerves Muscles of nerves Sweat skin arteriole glands walls Muscles constrict Skin arteries decrease constrict shivering secretion Less blood to the skin. Less radiation conduction of heat Less water covers the skin.
Normal Oxygen Levels Using a Pulse Oximeter LIVESTRONG.COM
What Is A Normal Resting Heart Rate by Adam Sharp Medium
New-Onset Heart Failure in a Patient With a Pacemaker An
Go2 Pulse Finger Oximeter - FREE Shipping
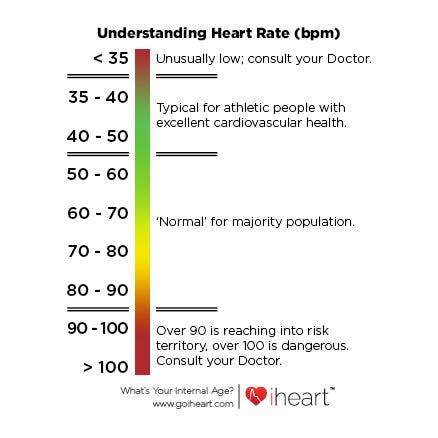
Pulse JVP
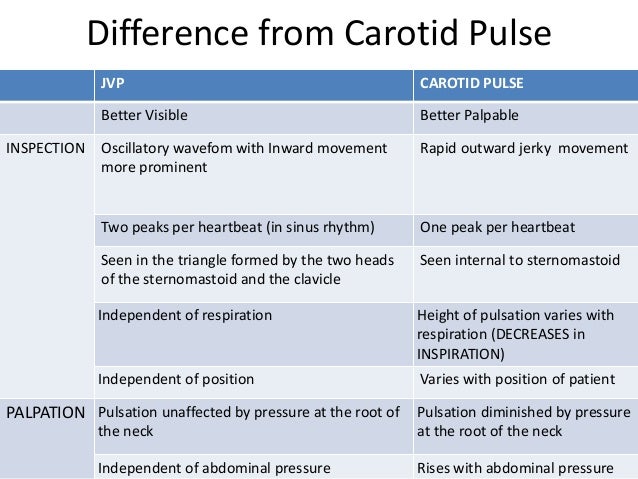
MRI of the Normal Bone Marrow Anatomic Sites Radiology Key
What is the Effect of Exercise on Heart Rate
Sylvania Nb501Sl9 Users Manual E5H26UD NB501SL9 EN
